Things to Understand Before Using 3D Scanning for Projects
Wiki Article
Checking out the Applications of 3D Laser Scanning in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Preservation
The assimilation of 3D laser scanning modern technology in archaeology and cultural heritage preservation notes a substantial innovation in exactly how historic sites and artifacts are recorded and analyzed. This non-invasive technique supplies specific spatial data, revealing intricate details that were previously tough to record. As the applications of this modern technology remain to advance, various ramifications for education and learning, documents, and preservation emerge, welcoming further exploration into its transformative effect on the area.Recognizing 3D Laser Scanning Modern Technology
3D laser scanning innovation has actually reinvented the field of archaeology by supplying exact and detailed spatial data. This sophisticated modern technology employs laser beam of lights to catch numerous information points from an item or website, creating a very accurate three-dimensional depiction (3D Scanning). The resulting point clouds can expose detailed details of historical sites, frameworks, and artefacts that could be unseen to the naked eyeUsing this innovation, archaeologists can document the specific measurements, forms, and placements of objects with extraordinary precision. This technique minimizes the threat of human mistake and gets rid of the demand for comprehensive hands-on dimensions. In addition, the information gathered can be assessed and shared easily, assisting in cooperation amongst scientists. By incorporating 3D laser scanning with GIS and various other digital tools, archaeologists enhance their ability to picture and interpret historic contexts, leading to deeper insights into old societies and environments.
Enhancing Archaeological Documentation
3D laser scanning substantially boosts archaeological documentation via its capacity to create accurate website maps. This modern technology assists in in-depth artefact analysis, giving insights that typical methods might neglect. On top of that, it guarantees the conservation of contextual information, which is essential for comprehending the partnerships within archaeological sites.Exact Site Mapping
While typical mapping methods frequently deal with capturing the detailed details of historical sites, progressed laser scanning innovation provides an advanced strategy to exact website mapping. This approach makes it possible for archaeologists to create very detailed and precise three-dimensional representations of sites, showcasing topographical variants and architectural functions with remarkable fidelity. The capability to record millions of data points in a matter of mins enables for detailed documents, which can be easily updated and shared amongst researchers. Furthermore, laser scanning helps with the measurement of intricate geometries that would be tough to assess utilizing conventional devices. Therefore, this innovation enhances the precision of website maps, adding substantially to the preservation and understanding of cultural heritage sources.In-depth Artifact Analysis
Laser scanning modern technology substantially enhances the analysis of archaeological artefacts, supplying scientists with unprecedented detail and precision. This technique catches complex surface structures, dimensions, and features that traditional documentation strategies might ignore. By producing high-resolution 3D designs, scholars can very closely check out artefacts without the risk of damage intrinsic in physical handling. This precision allows for better comparative research studies, making it possible for specialists to recognize production strategies, stylistic variations, and potential social relevance. Furthermore, the capability to manipulate and imagine information in 3 measurements assists in a deeper understanding of artefact capability and usage. Generally, laser scanning cultivates a much more extensive technique to historical documents, guaranteeing that vital details concerning artifacts is preserved for future research and education.Preservation of Contextual Information
Maintaining contextual data is necessary for improving archaeological documentation, as it assures that findings are recognized within their initial ecological and cultural frameworks. 3D laser scanning innovation greatly adds to this preservation effort by recording in-depth spatial relationships among artifacts, structures, and their environments. By generating precise 3D versions, archaeologists can record the exact locations and orientations of objects in situ, helping with a thorough understanding of their context. This technology allows scientists to review and assess sites long after excavation, preserving the integrity of contextual information. Additionally, electronic records created via scanning can be shared internationally, promoting collective study and public interaction. Eventually, protecting contextual data with 3D laser scanning enriches historical narratives and advertises a much more profound appreciation of cultural heritage.Preservation of Cultural Heritage Sites
As developments in technology remain to develop, the preservation of cultural heritage sites has actually ended up being significantly dependent on cutting-edge techniques such as 3D laser scanning. This technology permits the detailed documentation of artifacts, landscapes, and frameworks, recording their precise measurements and spatial relationships in a non-invasive way. By producing high-resolution 3D versions, scientists can analyze and monitor damage patterns, allowing proactive preservation methods.Additionally, 3D laser scanning helps with the sharing of detailed site data with the international area, advertising cooperation among conservationists, chroniclers, and excavators. These versions serve as invaluable resources for education and learning and public engagement, elevating awareness of cultural heritage problems. The digital documents produced can protect versus loss due to environmental aspects, criminal damage, or overlook. Overall, 3D laser scanning stands for a transformative method to the conservation of social heritage, guaranteeing that these websites can be examined and valued by future generations.
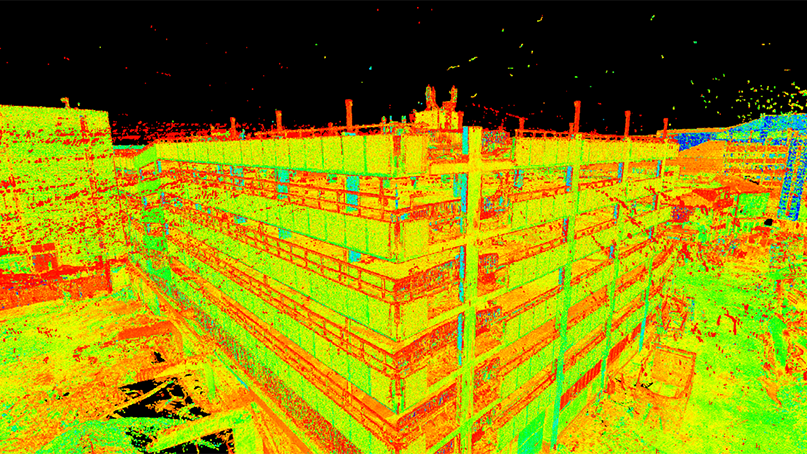
Restoration and Repair Efforts
The in-depth documents accomplished via 3D laser scanning plays a considerable function in repair and reconstruction efforts within archaeology. This innovation provides accurate measurements and high-resolution images, enabling for precise digital designs of structures and artifacts. These versions serve as vital recommendations during reconstruction procedures, making it possible for excavators to picture the original design and make notified choices about methods and materials needed for repair.Additionally, 3D laser scanning facilitates the reconstruction of harmed Recommended Site or lost components by producing in-depth reproductions. This process aids in making certain that repairs preserve historic stability while likewise enabling for ingenious techniques to recover websites. The capability to assess wear patterns and architectural weaknesses via checked information enhances understanding of a website's historic context and its usage with time. As a result, 3D laser scanning not just preserves the physical elements of cultural heritage but also enriches the story of history, directing future restoration undertakings.
Educational and Research Study Opportunities
The integration of 3D laser scanning in archaeology opens significant instructional and research study possibilities. Academic collaborations can boost the understanding of ancient websites, while specialized training workshops furnish professionals with vital skills for using this technology. Together, these initiatives foster a richer involvement with archaeological methods and methods.Academic Collaborations in Archaeology
Collective initiatives in archaeology have become significantly vital for progressing both academic and study possibilities. By fostering collaborations amongst universities, research institutions, and cultural heritage companies, these cooperations help with the exchange of expertise and resources, improving the top quality of historical studies. Joint projects often utilize diverse proficiency, permitting thorough evaluations and ingenious methodologies, particularly in the application of technologies like 3D laser scanning. Such cooperations likewise advertise interdisciplinary techniques, involving areas such as preservation, location, and history science. Furthermore, academic partnerships commonly cause the growth of brand-new curricula and training programs, preparing the next generation of archaeologists to effectively make use Our site of innovative innovations in their job. Inevitably, these alliances add to the preservation and understanding of social heritage.Educating Workshops for Experts
Training workshops for professionals in archaeology are significantly vital for enhancing skills in the application of sophisticated innovations such as 3D laser scanning. These workshops give individuals with hands-on experience in using innovative devices and software, promoting a deeper understanding of data capture and analysis procedures. Professionals can learn to produce exact digital models of historical sites, which considerably aid in paperwork and preservation efforts. Furthermore, these training sessions commonly include discussions on finest methods and study, advertising expertise exchange among individuals. By investing in continual education, professionals can stay upgraded on developing modern technologies, inevitably boosting the efficiency of their study and cultural heritage preservation efforts. This dedication to skill improvement is crucial for advancing the field of archaeology.Future Trends in 3D Laser Scanning for Archaeology
As developments in innovation continue to reshape different areas, the future of 3D laser scanning in archaeology guarantees to enhance both the precision and effectiveness of site documents and evaluation. Emerging trends indicate an expanding assimilation of synthetic knowledge and machine learning, facilitating automated information handling and analysis. This development will certainly enable excavators to evaluate intricate datasets faster, resulting in faster understandings into historical contexts.The assimilation of drone modern technology with 3D laser scanning is most likely to broaden, making it possible for extensive aerial studies of historical websites that are difficult to access. The increasing affordability of scanning tools will equalize accessibility, encouraging smaller sized organizations and independent scientists to make use of these devices successfully. Additionally, innovations in digital fact and enhanced fact will allow immersive experiences for public engagement and education, making archaeological findings much more easily accessible and interactive. These patterns jointly indicate a transformative future for archaeology, improving preservation initiatives and broadening the self-control's outreach.
Often Asked Concerns
Just How Much Does 3D Laser Scanning Tools Cost?
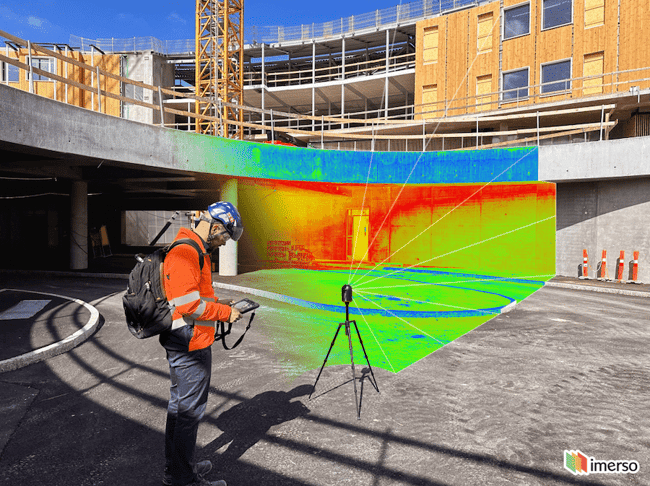

What Are the Limitations of 3D Laser Scanning?
The constraints of 3D laser scanning consist of high prices, possible data processing difficulties, sensitivity to environmental conditions, and problem catching elaborate information in complex surface areas, which can affect the accuracy and completeness of scanned representations. (3D Scanning)
Can 3D Laser Scanning Be Made Use Of Underwater?
Yes, 3D laser scanning can be made use of undersea, but it needs specialized tools and strategies to get over difficulties such as water distortion and limited exposure. Effective applications have been demonstrated in marine archaeology and underwater surveys.Just how Long Does a Scanning Job Normally Take?
A scanning job normally takes anywhere from a few days to a number of weeks, depending on the complexity and dimension of the location being checked, together with the preparation and post-processing requirements included in the task.Exist Particular Software Requirements for Processing 3D Checks?
Yes, details software demands for processing 3D scans include programs capable of dealing with large point clouds, such as Autodesk Wrap-up, Cyclone, or MeshLab. These devices facilitate evaluation, visualization, and assimilation into various applications efficiently.The integration of 3D laser scanning modern technology in archaeology and cultural heritage preservation notes a substantial advancement in how historic sites and artifacts are recorded and analyzed. published here 3D laser scanning modern technology has actually revolutionized the area of archaeology by providing exact and thorough spatial data. As innovations in modern technology proceed to progress, the conservation of social heritage sites has become significantly reliant on ingenious methods such as 3D laser scanning. As developments in technology continue to improve different fields, the future of 3D laser scanning in archaeology promises to enhance both the precision and effectiveness of website documents and evaluation. The combination of drone technology with 3D laser scanning is likely to increase, enabling comprehensive aerial studies of historical sites that are challenging to accessibility.
Report this wiki page